The activities under development at the ELEDIA@Innov’COM include (but are not limited to) the following main items:
- Wireless monitoring systems for precision farming application
- Semantic wireless localization and tracking
One of the common points between the above research topics is the innovative wireless sensor network (WSN) technology adopted to implement and validate the investigated solutions. The recent advances in autonomous and low-power wireless devices have facilitated the rapid diffusion of such technology, which presents disruptive advantages in a huge number of applications, thanks to its flexibility and adaptability to different practical requirements.
The state-of-the-art about distributed monitoring systems is full of WSN-based approaches and many open problems are still under study to improve the feasibility and the robustness of both the technological and methodological features of the systems.
The ELEDIA@Innov’COM Staff has long experience in the design and development of WSN-based systems, customized to satisfy the functional and non-functional requirements of the application at hand.
Precision Farming
The high quality of the Tunisian citrus fruits like lemons, clementines, Valencia variety, and mandarins is driving the worldwide export of such products.

The accurate management of citrus fruit farming is a key-action to maintain the quality standards of the product and guarantee the success of the export seasons.
In this framework, there is an increasing interest in the adoption of innovative technological solution for precision farming.
The ELEDIA Research Center has developed a WSN-based system for the continuous monitoring of the physical parameters that affect the cultivations. The real-time and distributed acquisition of soil parameters has been implemented through wireless sensors deployed in the fields. Such information can be exploited by farmers to understand the status of the plants and to intervene in the production process.
For example, the soil moisture level in combination with information about the weather conditions could improve the quality of the irrigation, the soil conservation, and the water saving. The activities of the ELEDIA@Innov’COM node aim to study and design a WSN-based monitoring system for the citrus fruit farming in real application environment. The Tunisian scenario represents a unique opportunity to test and improve the features of the investigated technologies and to customize the methodological approaches of data analysis.

Semantic Wireless Localization
The localization of moving targets is attracting great interest in a wide set of applications in the framework of smart cities and communities, and the diffusion of mobile wireless standards and devices has strongly stimulated the research of new and efficient location-based strategies. Both active and passive methods have been widely investigated according to the properties of the targets. Active methods process the wireless signal transmitted by a transceiver weared by the target, while passive solutions exploit the electromagnetic perturbations (measured through the received signal strength indicator) of the wireless propagation caused by the transceiver-free targets.
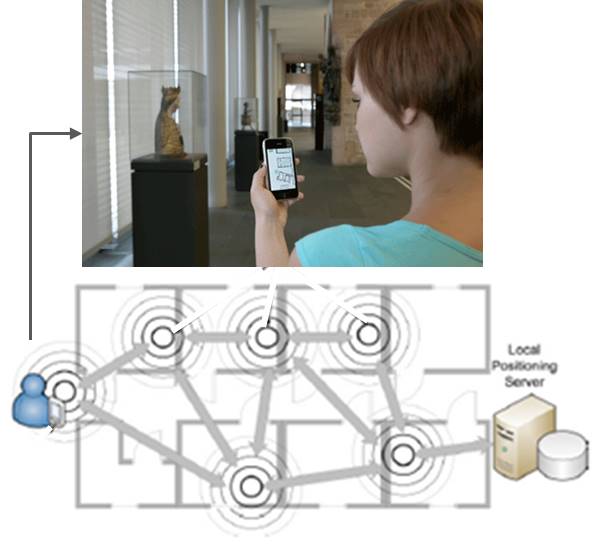
The properties of the environment have been also considered to improve the localization performance. The ELEDIA Research Center is involved in the study of the so-called Semantic Wireless Localization approach, which aims to understand the characteristics of the localization domain and the potential interactions with the target. The reconstruction of the domain map where the target is located and the extraction of the functional and logical information of the objects (e.g., fixed walls, open/closed doors, on/off appliances, forniture roles, etc.) change the interpretation of the localization from a geometrical point of view (e.g., ‘the target has been localized in position x,y’) to a semantic one (e.g., ‘the target is close to the desk’).
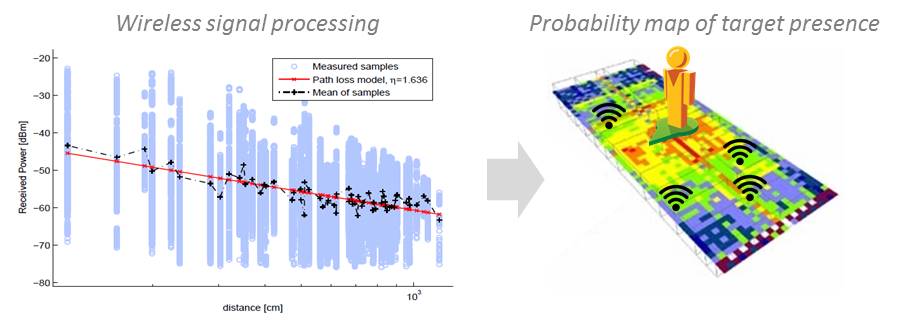
The activities developed by the ELEDIA@Innov’COM leverage the solid background on the localization methods studied by the involved members, including learning-by-example (LBE) strategies like neural networks, support vector machines, regression trees, gaussian processes, etc., able to learn the complex relation between the wireless signal behavior and the target position. The real-time performance make the LBE methods suitable for the efficient localization of different typologies of wireless devices, like the nodes of a WSN or the widely diffused WiFi-enabled smartphones.